In the dorsal horns or posterior horns many incoming sensory neurons synapse with interneurons which then distribute information to other parts of the spinal cord and brain. Posterior horn of the spinal cord.

Biology 164 Dolan Flashcards The Spinal Cord And Spinal Nerves Studyblue Spinal Cord Spinal Spinal Nerve
Tap card to see definition.

. The posterior horn posterior horn dorsal horn spinal dorsal horn of the spinal cord is the dorsal more posterior gray matter of the spinal cord. Click card to see definition. The interior of the cord is formed by gray matter which is surrounded by white matter Figure 111AIn transverse sections the gray matter is conventionally divided into dorsal lateral and ventral hornsThe neurons of the dorsal horns receive sensory information that enters the spinal cord via the.
These are linked by a thin gray commissure in which lies the central canal. It receives various types of sensory information from the body including light touch proprioception and vibration. It receives several types of sensory information from the body including fine touch proprioception and vibration.
The gray matter of the cord is butterfly-shaped with the so-called dorsal posterior horns forming the upper wings of the butterfly shape. Posterior part of gray matter Function. This information is sent from receptors of the skin bones and joints through sensory neurons whose cell bodies lie in the dorsal root ganglion.
The lateral horn that is only based in the thoracic upper lumbar and sacral regions is the central element of the supportive division from the autonomic central nervous system. The lateral horn which is only found in the thoracic upper lumbar and sacral regions is the central component of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system. Additionally what specific kind of cell lies in the lateral gray.
The posterior grey column of the spinal cord is one of the three grey columns of the spinal cord. As shown in Figure 1441 the gray matter is subdivided into regions that are referred to as horns. Posterior dorsal gray horns.
The gray matter is the area of the spinal cord where many types of neurons synapse. It receives several types of sensory information from the body. Different fiber types terminate in different lamina.
A thin strip of gray matter that surrounds the central canal of the spinal cord and along with the anterior white commissure connects the two halves of the cord. Spinal Cord Internal Structure- Gray matter. The anterior horn sends out motor signals to the skeletal muscles.
It contains the substantia gelatinosa. One of the divisions of the grey matter of the spinal cord the posterior horn contains interneurons that make connections within the spinal cord as well as neurons that enter ascending sensory pathways. Nucleus proprius- nucleus dorsalis clarckes column Click again to see term.
In the thoracic and upper lumbar segments the gray matter extends on both sides to form lateral hornsThe lower wings of the butterfly shape are. The dorsal horn the intermediate column the lateral horn and the ventral horn. The dorsal or posterior horn is divided in six layers laminae of grey matter with numbering starting at the dorsal-most edge.
The posterior horn or gray column of the spinal cord as appearing in cross section. The grey matter is divided into four main columns. The posterior horn is responsible for sensory processing.
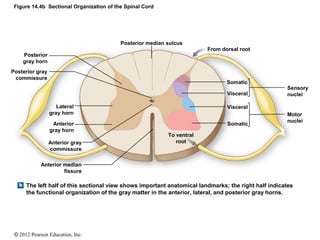
Posterior gray horn Posterior gray commissure Lateral gray horn Anterior gray horn Anterior gray commissure Anterior median fissure To ventral root Posterior median sulcus From dorsal root Sensory nuclei Motor nuclei Somatic Somatic Visceral Visceral. It contains the substantia gelatinosa. The dorsal horn also known as the posterior horn contains neurons that receive somatosensory information from the body which is then transmitted via the ascending pathways to the brain.
The posterior horn is responsible for sensory processing. The ventral horn also known as the. Tap again to see term.
The posterior horn TA or dorsal horn TAalt contains spinal laminae I-VI TA of Rexed. Fibers carrying noxious and thermal information tend to terminate superficially in laminae 1 and 2 whereas fibers carrying low-threshold mechanosensory information terminate more deeply. One of the divisions of the grey matter of the spinal cord the posterior horn contains interneurons that make connections within the spinal cord as well as neurons that enter ascending sensory pathways.
Gray Horns The posterior horn is responsible for sensory processing. The anterior horn sends out motor signals to the skeletal muscles. Contain cell bodies and axons of interneurons as well as axons of incoming sensory neurons.
The anterior horn sends out motor signals to the skeletal muscles. The posterior grey column posterior cornu dorsal horn spinal dorsal horn posterior horn sensory horn of the spinal cord is one of the three grey columns of the spinal cord. Sensory nuclei- somatic and visceral -receives information from skeletal muscles and skin somatic and visceral organs visceral and relays it to CNS.
It receives several types of sensory information from the body including fine touch proprioception and vibration. Gray Horns The posterior horn is responsible for sensory processing. The lateral horn which is only found in the thoracic upper lumbar and sacral regions is the central component of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system.
The nuclei of the posterior horn are the marginal nucleus TA nucleus marginalis TA gelatinous substance TA substantia gelatinosa TA nucleus proprius TA secondary visceral grey substance TA. Grey Horns The anterior horn transmits out motor signals towards the skeletal muscles. The anterior horn sends out motor signals to the skeletal muscles.
It contains the substantia gelatinosa. The posterior grey column posterior cornu dorsal horn spinal dorsal horn posterior horn of the spinal cord is one of the three grey columns of the spinal cord. The dorsal horn functions as an intermediary processing center for this information comprising a complex network of excitatory and inhibitory interneurons as well as projection neurons which transmit the processed somatosensory information from the spinal cord to the brain.
The functional organization of the gray matter in the anterior lateral and posterior gray horns. The arrangement of gray and white matter in the spinal cord is relatively simple. The lateral horn which is only found in the thoracic upper lumbar and sacral regions is the central component of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system.
One of the divisions of the grey matter of the spinal cord the posterior horn contains interneurons that make connections within the spinal cord as well as neurons that enter ascending sensory pathways. Spinal Cord Gray Matter Functions. What Is The Function Of The Lateral Gray Horn.
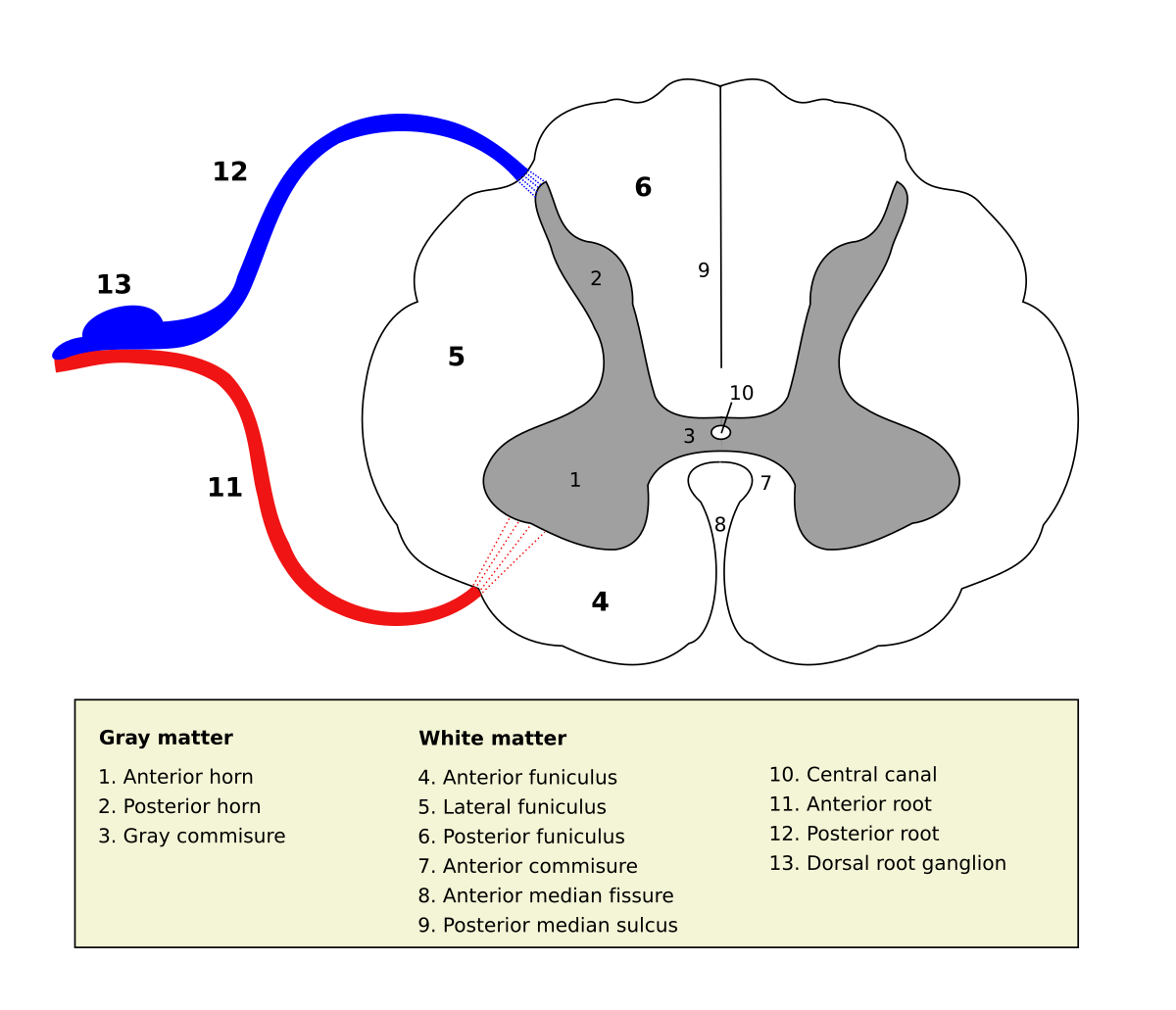
Posterior Grey Column Wikipedia
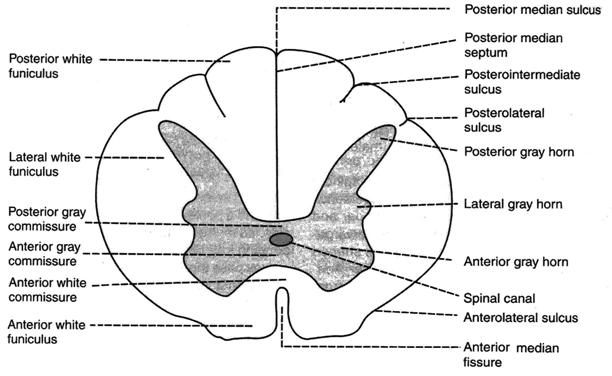
Neurons In Anterior Gray Horn Studopediya Net

14 4 The Spinal Cord Anatomy Physiology
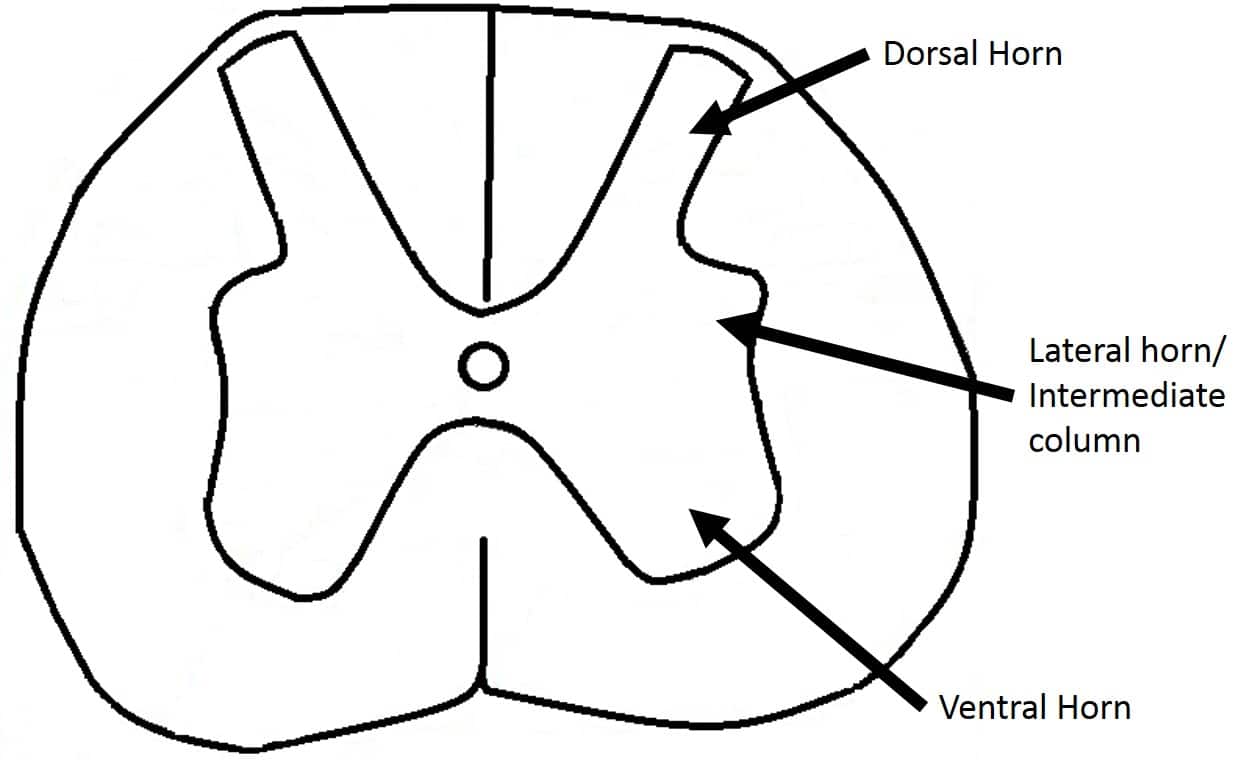

0 komentar
Posting Komentar